In a recent report titled “The Benefits and Opportunities of Ukraine’s EU Accession: The Strategic and Economic Implications of Ukraine’s EU Accession,” issued by the Tony Blair Institute for Global Change, the prospect of Ukraine joining the European Union emerges as a pivotal development with profound implications for Europe’s geopolitical landscape, particularly as the EU prepares to commence membership talks with Moldova and Ukraine on 25th June 2024.
The potential accession of Ukraine represents more than mere territorial expansion; it embodies a significant alignment with the EU’s core values amidst ongoing regional conflicts and challenges to sovereignty, writes Inna Chefranova.
The enduring war in Ukraine has not only challenged Europe’s stability but also highlighted its steadfast commitment to democratic principles and human rights amidst external aggression.
Strategically, Ukraine’s integration into the EU promises to bolster Europe’s security architecture and consolidate its role as a bastion of democratic governance.
However, this integration is not without complexities, necessitating substantial reforms both within Ukraine and across EU institutions. Key areas of reform include agricultural policies, institutional governance, and broader adjustments to accommodate Ukraine’s economic and political integration.
Economically, Ukraine stands to gain substantially from EU membership, particularly through enhanced trade opportunities.
Currently, the EU constitutes Ukraine’s largest trading partner, accounting for 56% of its trade in goods as of 2023.
Initiatives such as the “Solidarity Lanes” have facilitated robust trade relations, offering vital economic support amidst ongoing conflicts.
Projections suggest that EU membership could amplify Ukraine’s trade volumes significantly, with potential increases in imports and exports by 15% and 9%, respectively, by 2040, should membership be realised by 2030. Such growth not only fortifies Ukraine’s economy but also bolsters the EU’s global competitiveness and economic resilience.
Labour market dynamics are also poised for transformation, as Ukraine’s educated and skilled workforce integrates into the EU. Approximately 4.2 million Ukrainians currently benefit from temporary protection within the EU, contributing valuable human capital to sectors requiring skilled labour. This influx not only enriches the EU’s labour market but also supports Ukraine’s post-conflict reconstruction efforts.
Ukraine’s agricultural sector, renowned as the “breadbasket of Europe,” holds critical implications for regional food security. Integration into the EU could stabilise food prices and enhance agricultural sustainability, aligning with EU objectives while transforming the union into a significant exporter of cereals and grains.
Energy dynamics are similarly poised to evolve, with Ukraine’s substantial gas-storage capacity and renewable energy potential offering strategic advantages for the EU’s energy transition.
Ukraine’s natural resources, including critical raw materials essential for technological advancement, further solidify its potential role as a pivotal partner in Europe’s pursuit of strategic autonomy.
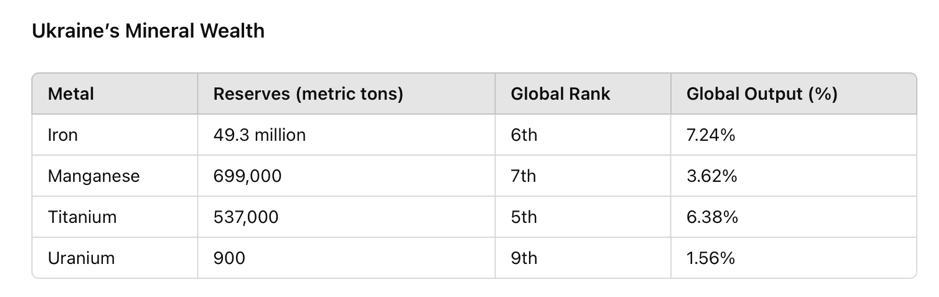
From a geopolitical perspective, Ukraine’s EU accession could serve as a stabilising influence in Eastern Europe, reinforcing regional security and cohesion. By setting a precedent for other Eastern European nations, Ukraine’s membership could promote broader stability while augmenting the EU’s governance structures and decision-making processes.
As negotiations progress, both Ukraine and the EU face critical decisions that will shape their future trajectories. The benefits outlined in the report highlight the potential for a mutually advantageous partnership, strengthening the EU’s global standing while reaffirming its commitment to democratic values and regional stability.
In conclusion, Ukraine’s path towards EU accession presents a transformative opportunity, offering economic prosperity, strategic alignment, and enhanced regional stability. As Europe navigates these pivotal developments, the strategic and economic implications underscore the significant stakes involved in Ukraine’s integration into the European Union.



